Four Students Are Determining the Probability of Flipping a Coin
Student Ana Brady Collin Deshawn Number of Flips 50 10 80 20 Which student is most likely to find that the actual number of times his or her coin lanc matches the predicted number of heads-up landings. The results are shown in the table.

Probability Two Coins Are Tossed Example Don T Memorise Youtube
To calculate the probability of event by flipping of two coins Then the sample space will be HH HT TH TT Total number of outcome 4.

. In this situation you have four coins that are all independent events. Probability of getting a head ½. Now use the sum command to compare the results from R experiments to the theoretical probabilities.
Elijahs prediction is high because 180 x 14 45. Hence the possibility that there should be two heads and two tails after tossing four coins is 38. Of times shown in the table below.
Coin toss probability formula for heads. Player 2 will get 1 point if the. Getting two heads out of 4 can be portrayed is disregarding order.
Then flip it 10 more times and combine the flips to determine the results for 20 flips. Students grades 4-8 will code an investigation to see how trial size impacts the probability of an event. In the above experiment of flipping a coin 4 times try to replicate the experiment 10 times and save the output as a vector.
Randomly choose an event Set the number of trials for an investigation. We can calculate probability by looking at the outcomes of an experiment or by reasoning about the possible outcomes. Number of possible outcomes 2.
Each flips a coin the number of times shown. In pairs both students flip their coins. Number of outcomes to get head 1.
Find the probability of At least two Heads. Heads is denoted by H. If the favorable outcome is tail T.
Calculate the probability of getting 3 heads out of 10 experiments using replicate andsum. P A Favorable outcomes Total number of outcomes. THE COIN-FLIPPING ACTIVITY To begin the activity each student has one coin or uses a random number generator.
How did the comparison of the results to the probability change. So in this case the correct calculation to determine the probability is. This shows that experimental probability is much more accurate for larger samples ie.
Player 1 will get 1 point if both flipped coins land either HH or TT. HHTT Hheads and Ttails Multiplying their probabilities will yield 054 but as for ordering we get 42cdot2 due to repetition which is the same as 4C2. Be sure they record each flip.
Larger number of. Four students are determining the probability of flipping a coin and it landing heads up. Flipping a Coin Students will code the computer to.
Correct answer - Four students are determining the probability of flipping a coin and it landing heads up. If you multiply the probability of each event by itself the number of times you want it to occur you get the chance that your scenario will come true. If the favorable outcome is head H.
The derivation of binomial probability. Correct answer to the question Four students are determining the probability of flipping a coin and it landing heads up. Four students each flip a coin multiple times and record the number of times the coin lands heads up.
Elijah is going to spin a spinner 180 times. Flip the coin 10 times and compare the actual results to the probability. In this case your odds are 210 9 10 4 1 10 6 0000137781 where the 210 comes from the number of possible fours of girls among the ten that would agree.
Assuming the coin to be fair you straight away answer 50 or ½. The probability of an event. Atmost one Heads and on tail.
The student will use their probability formula to determine that P12x1214 with each 12 being each flip 2 flips and the probability of flipping two heads is 1 out of 4 or 14. Therefore P getting heads fracnumber of favorable outcomestotal number of possible outcomes frac12 Coin toss probability formula for tails. Probability of occurring two heads and two tails 61638.
Clearly the favourable affair after tossing four coins are TTHH THTH THHT HTTH HTHT and HHTT. Probability tells us how likely something is to happen in the long run. Coin flips and die rolls.
Every flip of the coin doesnt depend on the other coin flips and we are dealing with a situation where one thing must occur as well as several other things. ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ 116. So we can conclude here.
So our answer is binom42cdot054 which is 0375. Theoretical and experimental probability. Flipping a coin 100 times vs.
But experiments work better with larger sample sizes eg. The group will flip the coin 3 times and determine the table of 3 flips using their own pattern and also write the probability of 3 flips. Therefore Number of favourable affair 6.
This is because you know that the outcome will either be head or tail and both are equally likely. Students will code this activity using Lynx at lynxcodingclub. To determine the experimental probability we could run an experiment in which we flip the coin 10 times and record the number of heads we get.
Have students investigate flipping a coin to determine likelihood of heads or tails. Of times shown in the table below. Ana Brady Collin Deshawn.
A number of favorable outcomes 1.
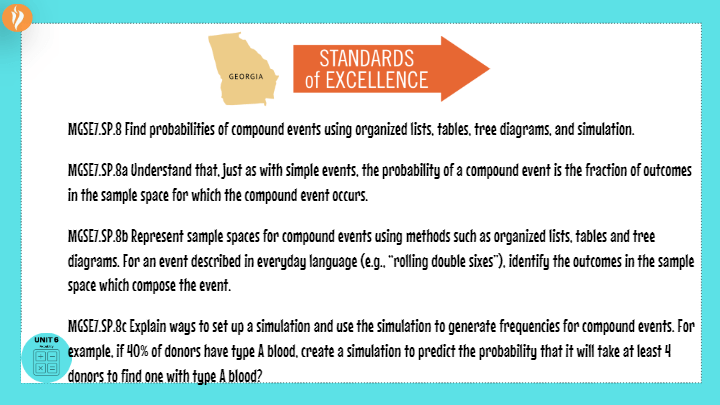
Tree Diagrams And Simulations Mathematics Quizizz

Probability Equal Likely Unlikely Certain Impossible Grade 3 Math Lesson Youtube 3rd Grade Math Math Lessons Probability Lessons

Find Probabilities Of A Binormal Distribution Coin Tosses Youtube

Question Video Determining The Relative Frequency Of An Event Nagwa

Tree Diagrams And Simulations Mathematics Quizizz

Probability Tossing Three Coins Tree Diagram At Least 2 Heads Youtube
A Coin Is Tossed 4 Times What Is The Probability That The Outcomes Of The Tosses Consist Of One Head And Three Tails Quora

Genetics Punnett Square Exit Ticket Assessments Differentiated Quizzes Key Punnett Squares Exit Tickets Quizzes

Four Students Are Determining The Probability Of Flipping A Coin And It Landing Head S Up Each Flips Brainly Com

Flip A Coin Learning Probability Worksheet Education Com Probability Worksheets Probability Math Probability Lessons

Question Video Determining The Set Of A Sample Space Of Flipping A Coin Nagwa

A Coin Is Tossed 4 Times Let X Denote The Number Of Heads Find The Probability Distribut Youtube

M02 Rend6289 10 Im C02 4 Teachingsuggestions Teaching Suggestion 2 Concept Of Probabilities Studocu
Probability Tree Diagrams Explained Mashup Math
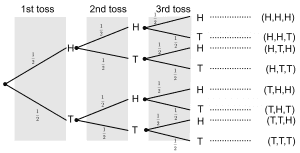
Coin Flip Probability Explanation Examples
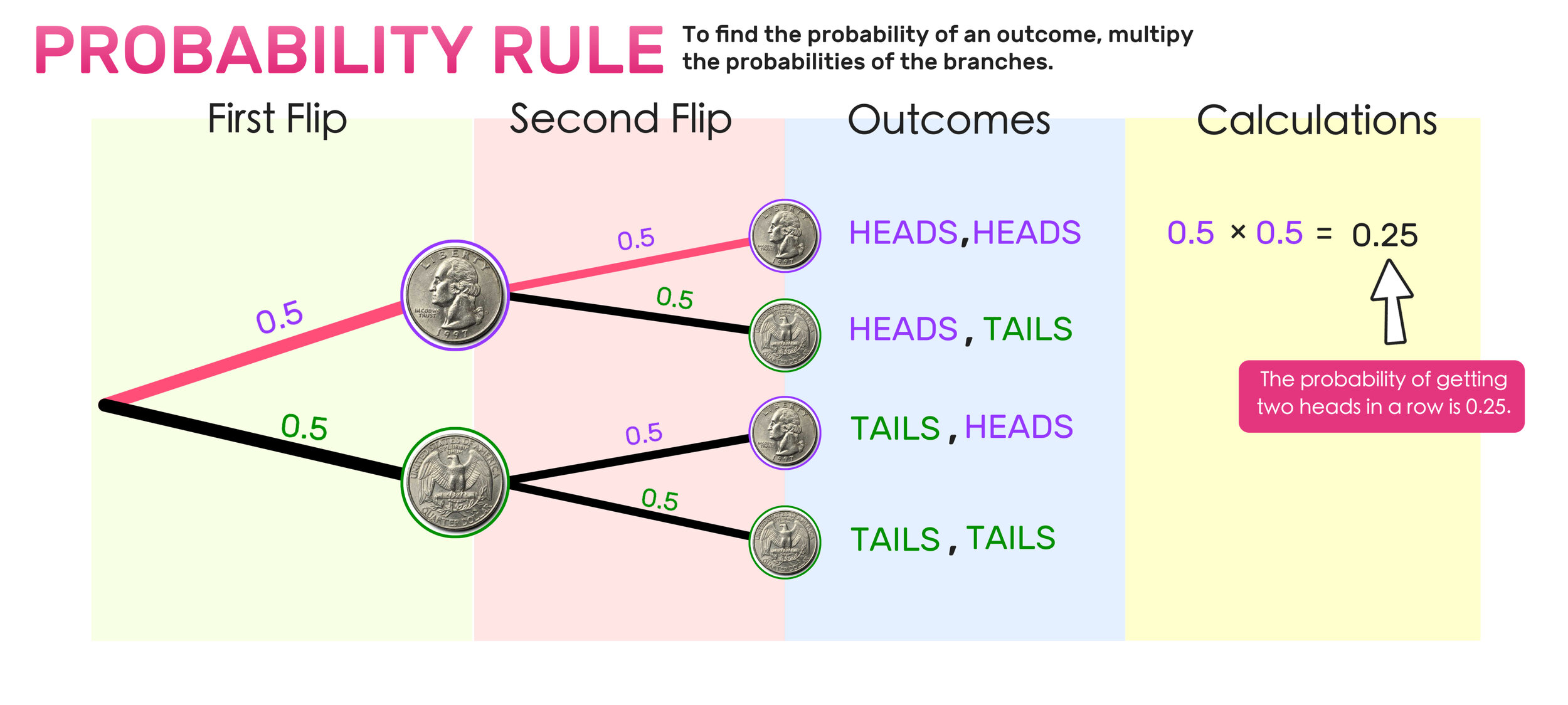
Probability Tree Diagrams Explained Mashup Math

Probability With Permutations And Combinations Google Forms Quiz 20 Problems Amped Up Learni Probability Lessons Permutations And Combinations Probability


Comments
Post a Comment